HCN, hydrogen cyanide, is a volatile and poisnous compound with distinguished bitter odor. It is linear molecule with a triple bond between C and N atom and has bond angle of 180 degrees. It can be found in fruits that have pits due to the fact that they contain small amounts of cyanohydrins which slowly releases hydrogen cyanide. Also it can be found in exhaust of vehicles and burning nitrogen-containig plastics.
The valence bond theory can be explained by overlapping of atomic orbitals which electrons are localized in the reigion to form chemical bonds. However, when you utilize this approach to explain chemical structure of the molecule, you must aware that there are various atomic orbitals for bonding which will significantly influence the structure of the molecule.
The Valence Bond thoery simply explains the bond formation just like lewis dot structure, but instead it explains the bonding in terms of covalent bond by quantum mechanics. According to this theory, bond will form when
Just like forming a molecule with lewis dot structure, bonds between atoms complete when two electrons share same orbital together.
Bond strength depends on the the amount of overlap since electrons are attracted to nuclei of both atoms, more electrons will pull more nuceli thus increase bond strength. However, two orbitals can not contian more than two atoms due to the maximum capacity it can hold.
Also, because known atomic geometry can not be able to have effective overlap, atomic orbitals combine with each other and reconfigure themselves into a different configuration. This process is called hybrdization.
This formation of new hybrid orbital is possible by combining several types of orbitals (s,p,d and etc).
HCN Lewis structure
Once you get the total number of valence electrons, you can make a Lewis dot structure of HCN. This structure helps in understanding the arrangement of valence electrons around the atoms in the molecule. It also aids with understanding the bonds formed in the molecule and the electrons not participating in any bond formation.
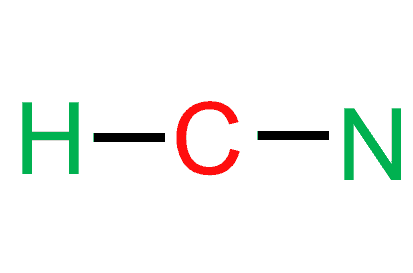
To start with making the Lewis Structure of HCN, we will first determine the central atom. And then place the remaining atoms in the structure.
As Carbon is the least electronegative atom in this molecule, it will take the central position. Place the Hydrogen and Nitrogen atoms on both terminal sides of the Carbon like this:
Once you have arranged the atoms, start placing the valence electrons around individual atoms. Like Hydrogen will have one electron, Carbon will have four electrons, and Nitrogen will have five electrons around its atom like this:
If you look at the structure closely, you will realize that Hydrogen can share one electron with the Carbon atom and become stable. So both Carbon and Hydrogen will share two electrons and form a single bond.
Now that we have completed the valence shell for Hydrogen let us do the same for the Carbon atom. The atom is left with only three valence electrons as it has shared one electron with Hydrogen. And so Carbon will share its remaining three electrons with Nitrogen to complete its octet, resulting in the formation of a triple bond between Carbon and Nitrogen.
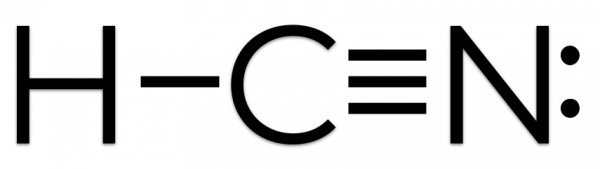
Carbon has a complete octet by forming a single bond with Hydrogen and a triple bond with the Nitrogen atom. Similarly, Nitrogen has a complete octet as it only needed three electrons for completing the octet that it got by sharing the electrons with Carbon. Hydrogen has two electrons in its outer valence shell. The rest two electrons are nonbonding electrons.
Step-by-Step Construction of Lewis Structure
The following are the steps to constructing the Lewis Structure.
Step 2: Determine the central atom
If we check the proper arrangement of C and N in the periodic table, we will find that the electronegativity values of C, N, and O are 2.5, 3.5, and 2.1. As per the rule, the atom with the least electronegative value should be at the structure’s center. Since hydrogen is the least electronegative, it can not take a central position. And due to the difference in electronegativities between carbon and hydrogen, the vector represents the charge that will be drawn from hydrogen to carbon. As carbon is a less electronegative atom than nitrogen in molecules, it will take the central position. Place the hydrogen and nitrogen atoms on both terminal sides of the carbon.
FAQ
Is HCN linear or tetrahedral?
